Processor Functions
Processor functions can be composed to a pipeline. Each function in a pipeline has to have a unique name.
If an error occurs during function execution or a validation fails, the unchanged input from the pipeline will be sent to the error topic. The message sent to the error topic will take two headers:
-
x-exception-message: The message text of the exception
-
x-exception-fqcn: The full qualified classname of the exception
hasValueValidator
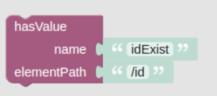
If the Json element at the given path does not have a value, an error is emitted.
Having a value means:
-
the element exists
-
the element value is not null
-
for a textual single value: the string is not empty
-
for a multivalue: the array contains at least one textual element which is not empty
Parameters
| Parameter Name | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
name |
String |
Yes |
The name of the function instance |
elementPath |
Yes |
The Pointer to the element to be checked |
trimNormalizer
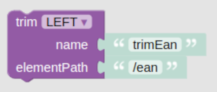
If the Json element at the given path is textual or an array containing textual elements, the trimNormalizer function will trim the textual content and return the Json content with the textual elements being trimmed. For arrays containing non-textual elements beside textual, the non-textual elements will be left untouched while textual elements will undergo a trim.
Parameters
| Parameter Name | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
name |
String |
Yes |
The name of the function instance |
elementPath |
Yes |
The Pointer to the element to be trimmed |
|
mode |
Enum |
Yes |
Determining the trim action. The validated content for mode is:
|
padNormalizer
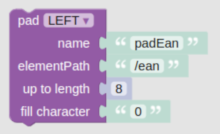
If the Json element at the given path is textual or an array containing textual elements, the padNormalizer function will add the determined character to the content to achieve a specific length and return the normalized Json. For arrays containing non-textual elements beside textual, the non-textual elements will be left untouched while textual elements will undergo the pad operation.
Parameters
| Parameter Name | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
name |
String |
Yes |
The name of the function instance |
elementPath |
Yes |
The Pointer to the element to be trimmed |
|
length |
Integer |
Yes |
The minimum length of textual elements
|
fillerCharacter |
Character |
Yes |
The |
pad |
Enum |
Yes |
Determining the side of adding the filler character. The validated content for pad is:
|
Match

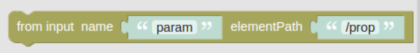
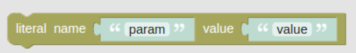
The Match function executes a search on an OpenSearch index to find entities in the index matching the function input.
The search utilizes an OpenSearch search template. The search template call can get named parameters, either a literal string or a value extracted from functions input.
The function result is a list of matched entities and the input used. The result fulfills the following schema:
{
"input": { /* Input Json content */ },
"matches": [ /* List of Matched entities */ ]
}Parameters
| Parameter Name | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
name |
String |
Yes |
The name of the function instance |
index |
String |
Yes |
The name of the OpenSearch index |
template |
String |
Yes |
The name of the OpenSearch search template |
paramsFromInput |
Map |
No |
The Notes: The search template should require these parameters and values. A sample:
|
literalParams |
Map |
No |
The Notes: The search template should require these parameters and values. A sample:
|
Example
Configuration
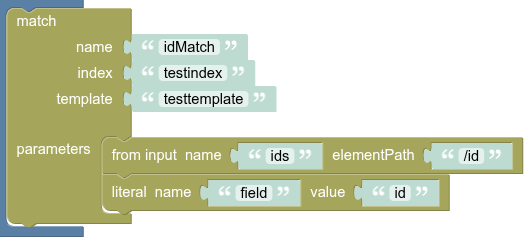
Function configuration:
index: testindex
template: testtemplate
paramsFromInput: [
Key: ids, Value: /id
]
literalParams: [
Key: field, Value: id
]
Search Template Sample:
{
"script": {
"lang": "mustache",
"source": "{\"query\":{\"terms\":{\"{{field}}\":{{#toJson}}ids{{/toJson}}}}}"
}
}Sample output of Match function
{
"input": {
"id": "1235",
"name": "sample-info"
},
"matches": [
{
"source": {
"id": "1235",
"name": "claas"
},
"id": "lghKxZYBh3Hgc5n0WdDk",
"score": 0.18232156
},
{
"source": {
"id": "1235",
"name": "sabine"
},
"id": "lwhNxZYBh3Hgc5n0mdA7",
"score": 0.18232156
}
]
}Reduce2One

The Reduce2One function usually gets its input from the Match function, and tries to solve the ambiguous match situation to reduce the matched entities to one entity, under these conditions:
-
If the
matcheselement only contains one item, it does nothing and passes the input as result. -
If the
matcheselement contains no item, it adds a matched entity with an emptysourceelement to thematches. -
If the
matcheselement contains more than one item, it returns the highestscorematched entity. (If thematcheselement contains more than one item with the highest score, it returns the first matched with the highest score.)
Note:
-
If the
matcheselement does not exist, or is not an array, theReduce2Oneraises an exception. -
If the
matcheselement contains more than one item, and one of these items does not contain thescoreelement, or thescoreelement is not numeric, it would be replaced with the default value equal to1.0
Parameters
| Parameter Name | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
name |
String |
Yes |
The name of the function instance |
Example
One item in the matches element
MergeCreate
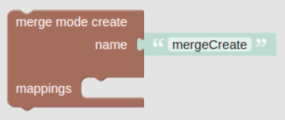

The MergeCreate function usually gets its input from the Match function, and tries to create elements from the input entity in the source-matched entity, under these conditions:
-
These changes only affect the first item in the
matcheselement. -
The
MergeCreateconfigurations determine which element of the input should be mapped into the source-matched entity. -
If the source-matched entity contains the mapped element that was determined in the function configuration, the
MergeCreatefunction does not touch it. -
If the source-matched entity does not contain the mapped element that was determined in the function configuration, the
MergeCreatefunction creates the element and fills it from the mapped element value of the input entity.
Parameters
| Parameter Name | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
name |
String |
Yes |
The name of the function instance |
mappings |
List |
Yes |
The list of mapping elements from input to the source-matched entity. Each item of the list contains 2 elements:
|
Example
Configuration
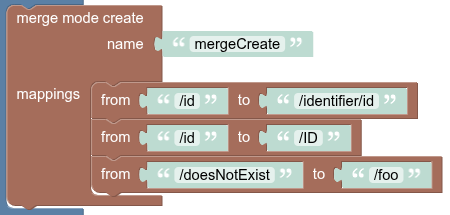
Function configuration:
mappings: [
from: /id, to: /identifier/id
from: /id, to: /ID
from: /doesNotExist, to: /foo
]
Input sample
{
"input": {
"id": "ID1"
},
"matches": [
{
"id": "match!",
"score": 1.0,
"source": {
"id": "TARGET_ID",
"identifier": {
"foo": 42
}
}
}
]
}Output sample
{
"input": {
"id": "ID1"
},
"matches": [
{
"id": "match!",
"score": 1.0,
"source": {
"id": "TARGET_ID",
"identifier": {
"foo": 42,
"id": "ID1"
},
"ID": "ID1"
}
}
]
}Note: As you can see in the Input and Output sample, if the input entity does not contain the from configured element, the MergeCreate function does nothing.
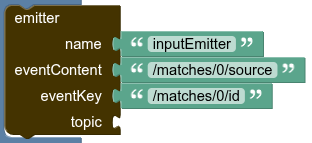
ChangeEventEmit


The ChangeEventEmit function extracts content and message key from the Json content of the message, and could emit the extracted message key and content in the normal output topic of the pipeline or a specific configured topic.
Parameters
| Parameter Name | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
name |
String |
Yes |
The name of the function instance |
eventContent |
Yes |
The |
|
eventKey |
No |
The |
|
topic |
String |
No |
The destination topic for emitted messages. Notes:
|
cleanUpMode |
enum |
No |
Determines the cleanup mode of the Notes:
|
cleanUpTimeHours |
int |
No |
Determine the cleanup time in hour of the Notes:
|
Multiple Functions
The Multiple Functions actually is an Operator, and it is not a real function.The Multiple Functions gets an input message and broadcasts it to each function inside the Multiple Functions.So the result would be similar to creating a fork in the pipeline.
Normally, Multiple Functions combined with ChangeEventEmit is used at the end of the pipeline for emitting different parts of input messages to different topics (please check the first example).However, the Multiple Functions can be used in more complicated scenarios throughout each part of the pipeline (please refer to the second example).
Example
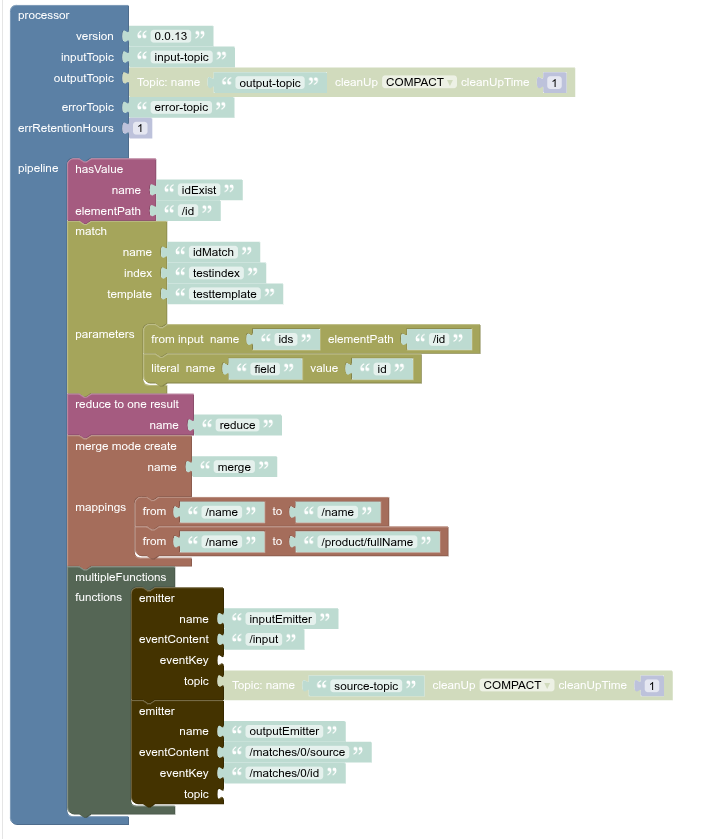
Using a single Multiple Functions at the end of a pipeline
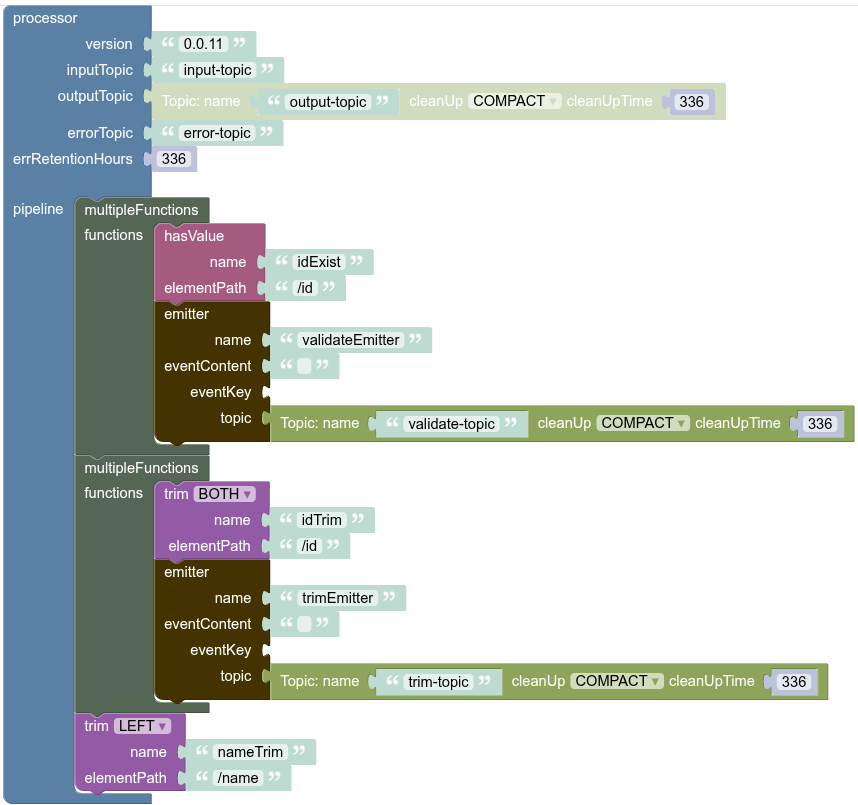
Using several Multiple Functions in different parts of a pipeline
Sample input messages in the input-topic
1: {"id":[], "name":"name0"}
2: {"id":[" ID1 "], "name":" name1 "}
3: {"id":["ID2"], "name":"name2"}
Sample output messages to the output-topic
1: {"id":["ID1"],"name":"name1"}
2: {"id":["ID2"],"name":"name2"}
Sample output messages to the validate-topic
1: {"id":[],"name":"name0"}
2: {"id":["ID1"],"name":"name1"}
3: {"id":["ID2"],"name":"name2"}
Sample output messages to the trim-topic
1: {"id":[],"name":"name0"}
2: {"id":[" ID1 "],"name":"name1"}
3: {"id":["ID2"],"name":"name2"}
4: {"id":[" ID1 "],"name":"name1"}
5: {"id":["ID2"],"name":"name2"}
And in the diagram below, you can see the state of messages in these three paths:
-
Main Route: Between
input-topicandoutput-topic, and error pushed to theerror-topic -
Validate Route: created by
validateEmitterand messages pushed to thevalidate-topic -
Trim Route: created by
trimEmitterand messages pushed to thetrim-topic